The Evolution of Marketing Psychology: From Instinct to Science

Marketing has always revolved around understanding the consumer. Early marketing efforts depended on instinct and general assumptions about public appeal. Over time, however, the psychology of marketing developed into a more scientific field.
This evolution represents a significant shift. It moved from basic persuasion to a much deeper understanding of human behavior and what motivates people.
The Pioneers of Marketing Psychology
The early 1900s saw the rise of individuals who recognized the power of psychology to influence consumer choices. Businesses often use a CRM system to manage customer relationships effectively. A CRM helps businesses collect valuable data and learn about customer preferences, behaviors, and motivations. This data-driven approach is essential for understanding the psychology of marketing. It also allows businesses to tailor campaigns for specific target audiences. Edward Bernays, a nephew of Sigmund Freud, is considered a pivotal figure in this era. Often called the “father of public relations,” Bernays used psychological principles in advertising campaigns in the 1920s.
His Lucky Strike cigarette campaign is a prime example. By framing cigarettes as “torches of freedom,” the campaign appealed to the growing women’s liberation movement. This tactic effectively broke down social barriers against women smoking. It demonstrates the impact of connecting with deeper desires and cultural shifts. You can learn more about the use of psychology in early marketing here.
From Theory to Practice
These initial applications of psychology laid the groundwork for a more structured approach to marketing psychology. Marketers began incorporating established psychological theories into their strategies. This meant going beyond simple emotional appeals. It required considering the cognitive processes involved in decision-making.
The Modern Landscape: Data and Neuroscience
Today, the psychology of marketing has become incredibly advanced. Access to vast amounts of data allows marketers to analyze consumer behavior with remarkable accuracy. Neuromarketing adds yet another layer of complexity. Using tools like EEG and eye-tracking, neuromarketing provides insight into subconscious consumer responses. This lets marketers understand not only what consumers say they want, but also how they react to different marketing stimuli.
This progression has transformed marketing. It is now a dynamic, data-driven field, continually adapting to new discoveries in human behavior. Further exploration of marketing psychology promises even more effective and engaging marketing campaigns in the years to come.
Visual Psychology: Why Your Brain Can’t Resist Certain Designs
Visuals are incredibly important in marketing. They constantly influence our choices as consumers, often without us even realizing it. This means understanding how visuals work is key to creating effective marketing campaigns.
The Science of Visual Appeal
Why are some designs so captivating? It all comes down to how our brains process what we see. We’re naturally drawn to certain shapes, colors, and arrangements. This is visual psychology in action, and it’s the key to creating marketing materials that truly resonate. By understanding these principles, you can create designs that grab attention and boost engagement.
Color Psychology: More Than Just Aesthetics
Color is about much more than just making things look pretty. It’s a powerful communication tool. Different colors create different feelings and associations. Think about the calming effect of blue, often used to represent trust and stability, or the energy of red, which can signal excitement or urgency. Choosing the right colors is crucial for aligning your visuals with your brand message and target audience.
The Impact of Color and Design
Design and color have a profound impact on marketing. Studies show a staggering 94% of first impressions are design-related. Even more compelling, 85% of consumers say color is the main reason they buy a product. Clearly, visual appeal is a driving force in consumer behavior. For more insights into these statistics, check out this resource: Marketing Psychology Statistics.
The Power of Shapes and Layouts
Shapes and layouts are also key players in visual perception. Rounded shapes often convey a sense of softness and friendliness, while sharp angles project strength and dynamism. These subtle cues can significantly influence how consumers perceive your brand. A well-organized layout can guide the viewer’s eye to essential information, creating a positive and effective user experience.
Putting Visual Psychology Into Practice
So how can you apply these principles to your marketing efforts? The first step is understanding the psychology behind visual preferences. This allows you to create designs that truly connect with your target audience. Experimentation is also essential. Test different colors, shapes, and layouts to discover what resonates best with your audience. The following table, “Psychological Impact of Colors in Marketing”, dives deeper into these color associations.
To illustrate the practical application of color psychology, the following data chart visualizes click-through rates from a recent A/B testing campaign, exploring the impact of different color schemes.

The data chart reveals that Color Scheme B (red and yellow) had the highest click-through rate at 8%, significantly outperforming the other schemes. This suggests that this color combination effectively captured attention and encouraged clicks.
To understand how color influences consumer behavior, let’s look at the psychological effects of different colors in marketing. The table below provides examples of how brands leverage color psychology to create specific emotional connections.
| Color | Psychological Effect | Emotions Evoked | Brand Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blue | Trust, Stability, Security | Calm, Peaceful, Reliable | Facebook, Twitter, American Express |
| Red | Excitement, Urgency, Passion | Energetic, Bold, Aggressive | Coca-Cola, Target, McDonald’s |
| Green | Nature, Growth, Health | Fresh, Tranquil, Soothing | Starbucks, Whole Foods Market, Subway |
| Yellow | Optimism, Happiness, Creativity | Cheerful, Playful, Friendly | Best Buy, Nikon, IKEA |
| Orange | Enthusiasm, Playfulness, Creativity | Warm, Inviting, Energetic | Nickelodeon, Fanta, Harley-Davidson |
This table highlights how strategic color choices can strengthen brand identity and influence purchasing decisions. By understanding the emotional impact of color, marketers can create more effective campaigns. The superior performance of Color Scheme B underscores the power of visual psychology in achieving tangible marketing results.
Values-Based Marketing: The Authentic Connection Advantage

Today’s consumers are increasingly drawn to brands that reflect their personal values. This represents a significant shift in the psychology of marketing. It’s no longer enough to simply highlight product features and benefits. Brands must now build authentic connections by aligning with the causes their customers care about.
Identifying Authentic Values
The key challenge for businesses is identifying the values that genuinely resonate with their target audience. This requires a deep understanding of their customer base and what motivates them. Authenticity is paramount. Consumers can quickly spot performative activism, which can severely damage a brand’s reputation. Aligning with values must be a genuine reflection of the company’s core beliefs and actions.
Communicating Values Effectively
Once core values are identified, businesses must communicate these commitments in a way that builds trust. Transparency is crucial. Clearly explaining how the brand supports its chosen values – through concrete actions and initiatives – helps avoid consumer skepticism. This might involve highlighting sustainable practices, supporting relevant social causes, or promoting ethical sourcing. The goal is to demonstrate a genuine commitment, fostering stronger relationships with customers who share those values.
Measuring the Impact of Values Alignment
The connection between brand values and consumer preferences plays a significant role in the psychology of marketing. For instance, a growing number of millennials prefer brands that align with their values. A 2018 Forbes survey indicated that roughly 60% of millennials favor products from value-aligned brands. Learn more about the psychology of marketing here. This highlights how marketing can effectively tap into the psychological desire for identity and social responsibility, especially among younger demographics.
Building Trust and Loyalty Through Values
By aligning products with ethical and moral values, companies can build strong emotional bonds with their customers, ultimately increasing brand loyalty. This goes beyond simple transactions; it’s about cultivating a sense of shared purpose and building a community around shared values. Values-driven marketing emphasizes creating a positive impact, both for the consumer and the wider world.
Case Studies: Navigating Values-Based Marketing
Numerous brands successfully navigate the complexities of values-based marketing. Patagonia consistently demonstrates its commitment to environmental sustainability, attracting a loyal customer base that shares this concern. Similarly, TOMS Shoes’ “One for One” model resonated with customers who valued the company’s social impact. These examples demonstrate how aligning with authentic values creates a competitive advantage. It not only strengthens customer relationships but also positively impacts the bottom line. Analyzing these case studies provides valuable insights for businesses seeking to integrate values into their marketing strategies. This allows them to forge meaningful connections with customers based on shared beliefs and a commitment to positive change.
Cognitive Biases: The Invisible Forces Driving Customer Decisions
Building on the core principles of values-based marketing, let’s explore cognitive biases. These mental shortcuts influence our decisions, often without us even realizing it. Understanding these biases is crucial for effective marketing. It helps create campaigns that resonate with how people actually think.
Anchoring Bias: Setting the Stage for Perception
The anchoring bias describes how we overemphasize the first piece of information we receive (the “anchor”). Imagine a customer sees a high initial price for a product. Even if it’s later discounted, they’ll likely still perceive it as more expensive than if they saw the lower price first. Marketers can use this by strategically presenting prices or highlighting a product’s original value.
Loss Aversion: The Fear of Missing Out
Loss aversion is the principle that the pain of a loss is felt more strongly than the pleasure of an equal gain. This means framing your marketing messages around what customers stand to lose can be more impactful than focusing on potential gains. Limited-time offers and highlighting scarcity are common tactics.
The Paradox of Choice: Simplifying Decisions
Too many choices can be overwhelming. This is the paradox of choice, and it can lead to indecision and even buyer’s remorse. A customer faced with numerous similar products might choose nothing at all. By curating product selections and simplifying the buying process, marketers can reduce this cognitive overload.
Confirmation Bias: Reinforcing Existing Beliefs
Confirmation bias is our tendency to favor information that confirms our existing beliefs. A customer who believes a brand is high-quality will be more receptive to marketing that reinforces that perception. This highlights the importance of a strong brand reputation.
To illustrate these biases and their impact on marketing, let’s look at the following table:
Key Cognitive Biases in Marketing Psychology: A comprehensive overview of the most influential cognitive biases affecting consumer behavior, with marketing applications and examples
| Cognitive Bias | Psychological Mechanism | Marketing Application | Effectiveness Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anchoring Bias | Over-reliance on the first piece of information received | Setting initial prices high, then offering discounts; highlighting original value | High |
| Loss Aversion | Feeling the pain of a loss more strongly than the pleasure of an equivalent gain | Limited-time offers; emphasizing scarcity; framing messages around potential losses | High |
| Paradox of Choice | Overwhelmed by too many options, leading to inaction | Curating product selections; simplifying the buying process; offering personalized recommendations | Medium |
| Confirmation Bias | Favoring information that confirms existing beliefs | Building a strong brand reputation; targeting marketing messages to reinforce positive perceptions | Medium |
This table summarizes how understanding these biases allows marketers to craft more persuasive campaigns.
The Power of Cognitive Biases
Recognizing these biases can significantly improve marketing effectiveness. By understanding these natural thought patterns, you can create campaigns that resonate more deeply. It’s important to use these principles ethically, guiding customers towards beneficial choices, rather than manipulating them. This builds trust and long-term loyalty.
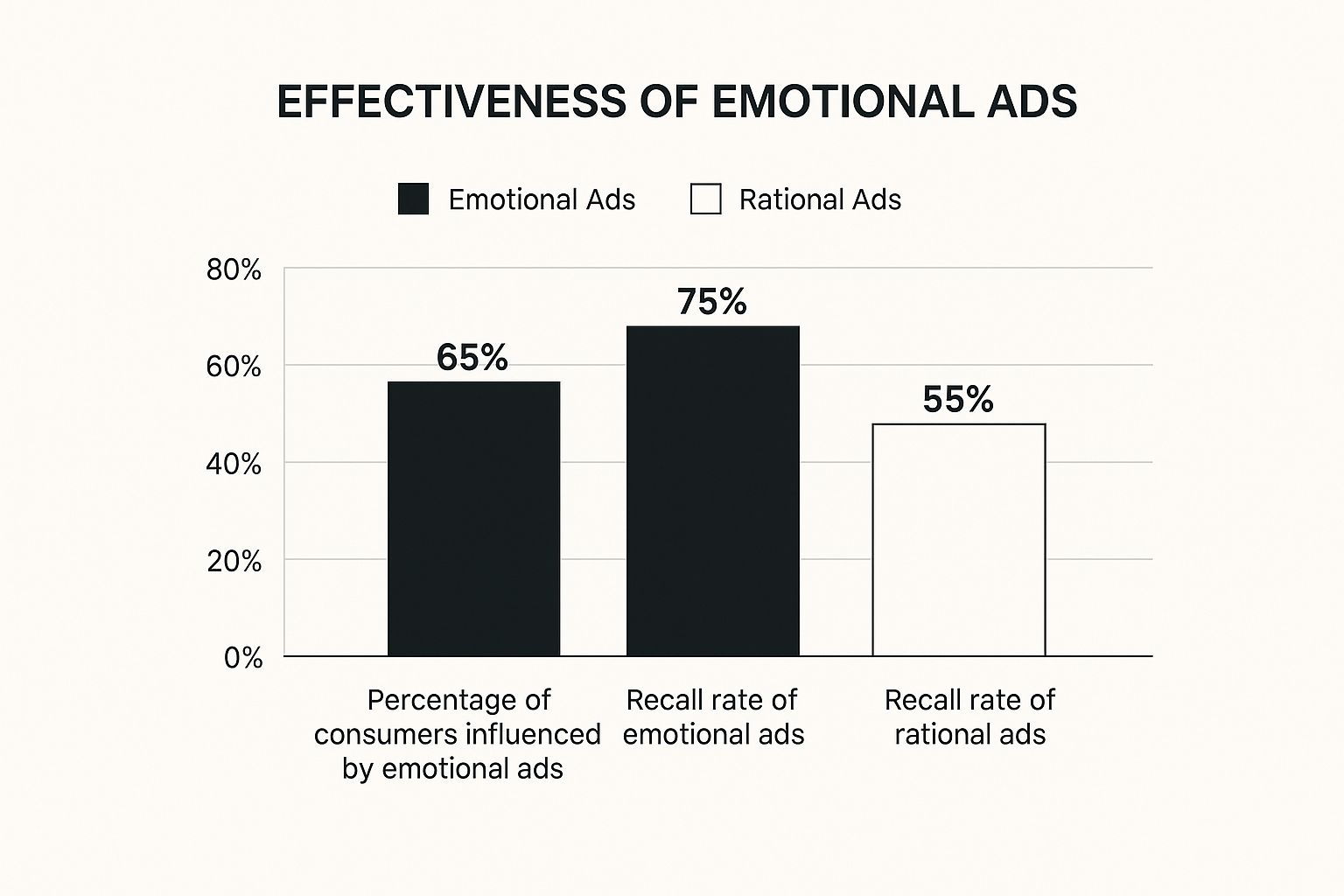
Emotional Marketing: The Science of Memorable Brand Experiences

While cognitive biases affect our rational thinking, emotional marketing focuses on the impact of feelings. This facet of the psychology of marketing acknowledges that buying decisions are rarely based purely on logic.
Instead, our emotions often play a significant role. Creating truly memorable brand experiences means understanding and utilizing these emotional connections.
The Neuroscience of Emotional Decision-Making
Our brains are hardwired to react to emotions. Experiencing something positive triggers the release of dopamine, creating a feeling of reward. This positive reinforcement can heavily influence our brand preferences and buying choices.
On the other hand, negative emotions can lead customers to avoid a brand and create a negative perception. Understanding the neuroscience behind emotions is essential for developing effective marketing strategies.
Emotional Triggers and Consumer Behavior
Different emotions influence consumer behavior in various ways. Nostalgia, for instance, can establish a strong connection with a brand by reminding us of happy memories.
This emotional trigger is especially effective when marketing to older demographics. Aspiration, conversely, can encourage consumers to buy products or services seen as enhancing their status or lifestyle. This tactic works well for luxury items or self-improvement products.
Understanding these emotional triggers allows marketers to craft targeted messages that resonate with their audience throughout their purchasing journey.
Mapping Emotional Touchpoints
Building positive emotional experiences requires careful consideration of every interaction a customer has with your brand. These emotional touchpoints can include website visits, social media interactions, customer service experiences, and even product packaging.
Mapping these touchpoints helps identify opportunities to build and strengthen positive emotional connections. A personalized thank you note after a purchase can foster a sense of appreciation.
Likewise, efficient and helpful customer service can reduce frustration and build trust.
Testing Emotional Resonance
Assessing the effectiveness of emotional marketing necessitates testing. Analyzing customer feedback and reviews can reveal patterns in emotional responses to specific campaigns.
A/B testing different marketing messages, adjusting emotional tone and language, can pinpoint the most effective approach. This data-driven approach relies on actual consumer responses, not assumptions, to guide emotional appeals.
Building Long-Term Brand Loyalty Through Emotion
Emotional marketing goes beyond simply increasing sales. It’s about building lasting brand loyalty. By consistently providing positive emotional experiences, businesses can create strong bonds with customers.
This connection transcends individual transactions, fostering a sense of community and shared values. Emotionally connected customers are more likely to become repeat buyers and brand advocates, fueling sustained business growth.
Maintaining consistent emotional messaging across all platforms strengthens a cohesive brand identity, reinforcing the desired emotional association and deepening customer loyalty.
Neuromarketing: Inside the Consumer’s Mind (Literally)
Neuromarketing explores the fascinating connection between neuroscience and marketing. It aims to understand consumer behavior at a subconscious level, digging deeper than traditional market research methods like surveys and focus groups. This provides a more accurate and less biased view of what truly motivates purchasing decisions.
Exploring Neuromarketing Techniques
Several key technologies are central to neuromarketing research. EEG (electroencephalography) measures brainwave activity to reveal insights into emotional and cognitive responses. Eye-tracking shows where consumers focus their visual attention, highlighting the most appealing elements of ads or packaging. Facial coding analyzes micro-expressions to uncover emotional reactions, providing a deeper understanding of consumer sentiment.
These techniques offer powerful tools for understanding the psychology of marketing. However, they also raise important ethical considerations. Consumer privacy and informed consent are crucial when using these technologies. The objective is to understand, not manipulate, consumer behavior.
Actionable Insights from Neuromarketing
While the sophisticated equipment used in formal neuromarketing studies might seem out of reach, businesses of all sizes can apply these principles. For instance, understanding how color influences emotions can guide website design and branding. Knowing that consumers are drawn to faces in images can optimize ad placement for maximum impact.
Even without specialized tools, grasping these basic principles allows businesses to craft more effective marketing campaigns. By considering how the brain processes information and makes decisions, companies can enhance marketing materials and elevate the overall customer experience.
The Hype vs. Reality of Neuromarketing
Neuromarketing offers valuable insights, but it’s important to distinguish genuine potential from overblown claims. Some techniques are more reliable and yield more actionable data than others. Eye-tracking, for example, has proven effective in understanding how consumers visually engage with websites and products, leading to practical improvements in website design.
Interpreting complex brainwave data from EEG, however, can be difficult. It requires specialized expertise to identify meaningful patterns amid the noise. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each technique, businesses can make informed choices about the methods best suited to their needs.
Ethical Considerations in Neuromarketing
The power of neuromarketing techniques demands careful ethical consideration. Respecting consumer autonomy is paramount. Businesses must prioritize transparency and avoid manipulating consumer behavior.
Obtaining informed consent is essential for any neuromarketing study. Consumers must understand how their data will be used and how their privacy will be protected. By adhering to ethical guidelines, businesses can responsibly leverage the benefits of neuromarketing.
Ready to boost your brand credibility and improve your digital marketing performance? Notifyio provides actionable insights and expert perspectives on the power of social proof and conversion optimization. Visit Notifyio today to learn more.




Leave a Reply